4.2 N维数组-ndarray
学习目标
- 目标
- 说明数组的属性,形状、类型
- 应用
- 无
1 ndarray的属性
数组属性反映了数组本身固有的信息。
| 属性名字 | 属性解释 |
|---|---|
| ndarray.shape | 数组维度的元组 |
| ndarray.ndim | 数组维数 |
| ndarray.size | 数组中的元素数量 |
| ndarray.itemsize | 一个数组元素的长度(字节) |
| ndarray.dtype | 数组元素的类型 |
2 ndarray的形状
首先创建一些数组。
# 创建不同形状的数组
>>> a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
>>> b = np.array([1,2,3,4])
>>> c = np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]])
分别打印出形状
>>> a.shape
>>> b.shape
>>> c.shape
(2, 3) # 二维数组
(4,) # 一维数组
(2, 2, 3) # 三维数组
如何理解数组的形状?
二维数组:
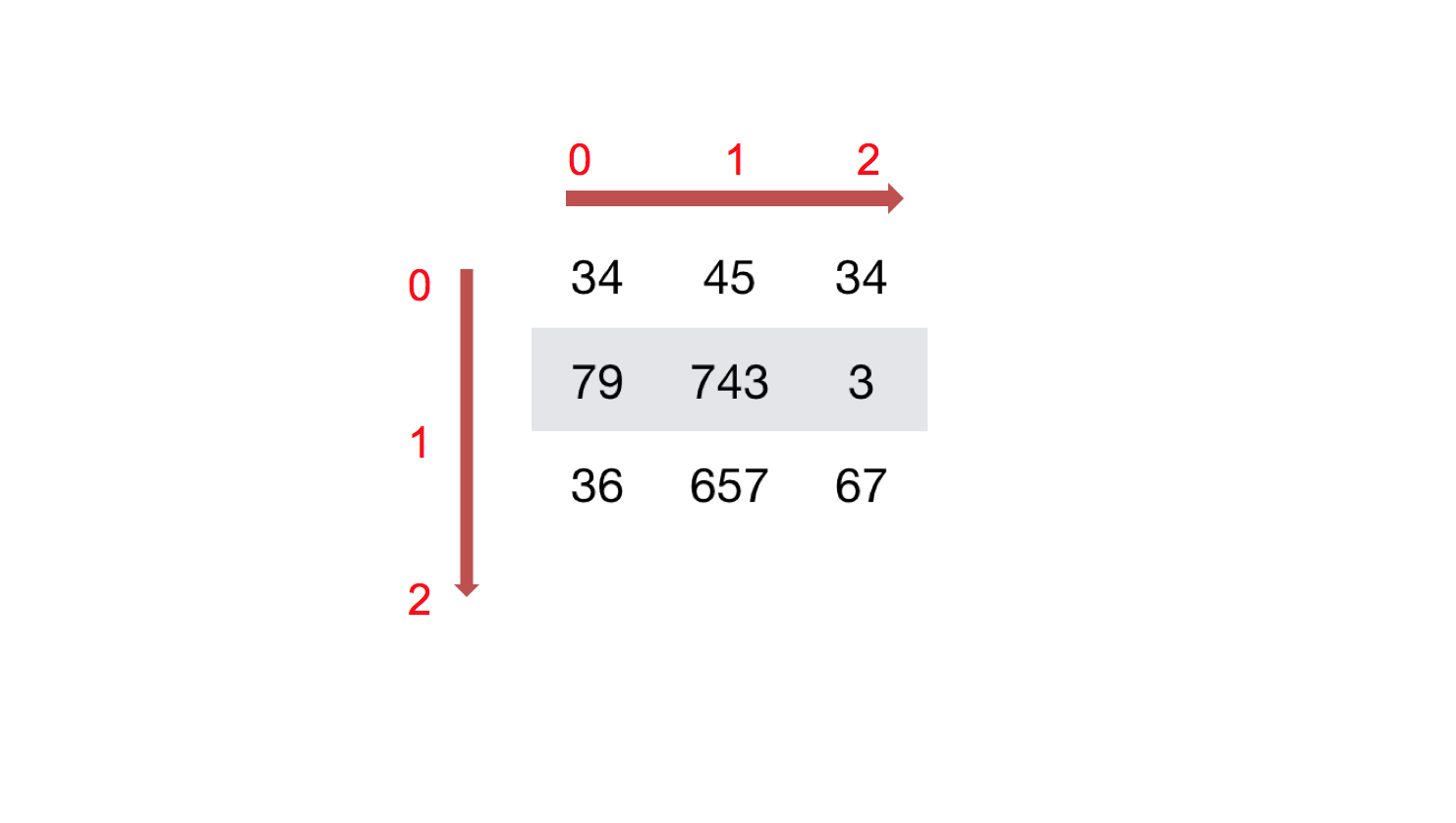
三维数组:
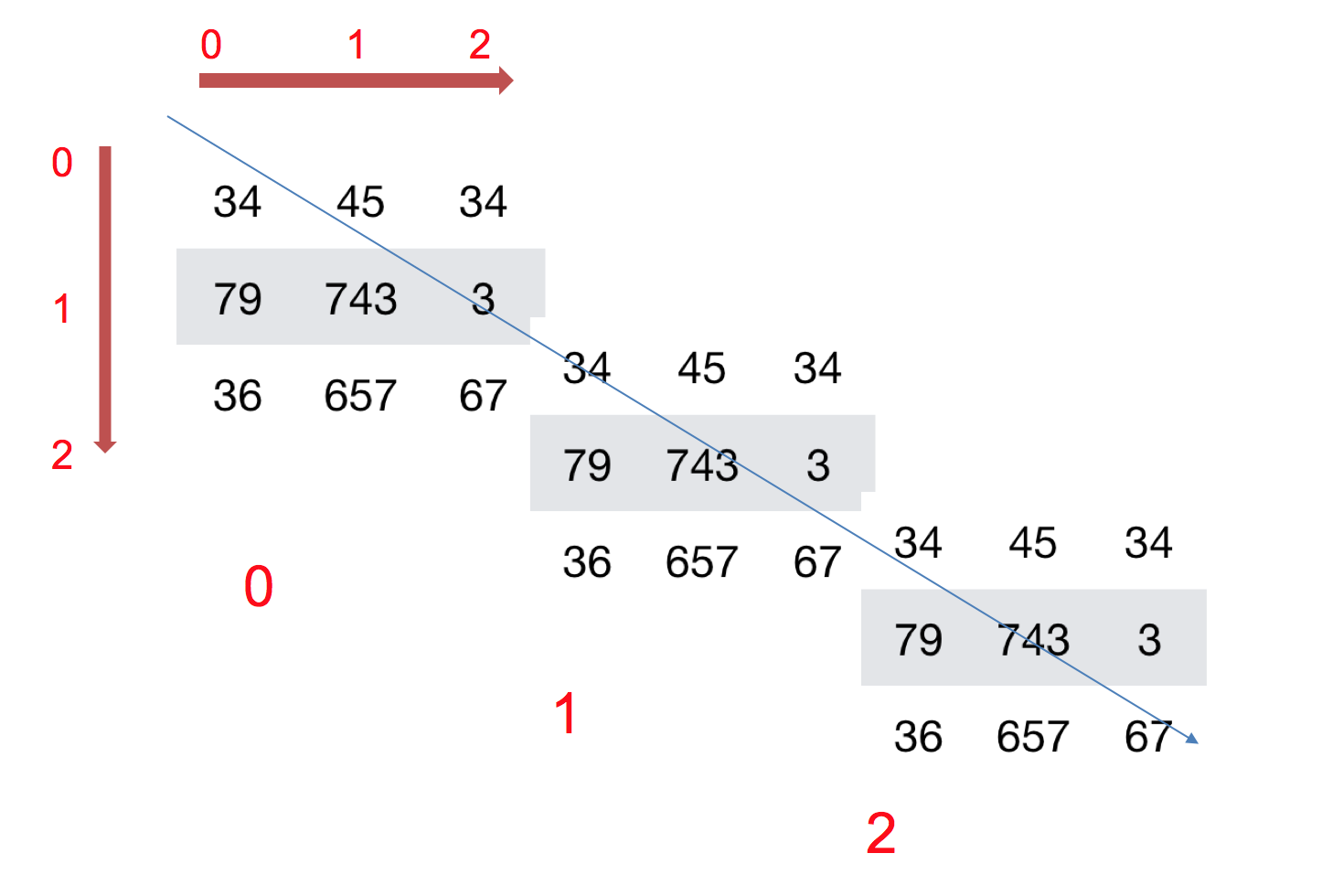
3 ndarray的类型
>>> type(score.dtype)
<type 'numpy.dtype'>
dtype是numpy.dtype类型,先看看对于数组来说都有哪些类型
| 名称 | 描述 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| np.bool | 用一个字节存储的布尔类型(True或False) | 'b' |
| np.int8 | 一个字节大小,-128 至 127 | 'i' |
| np.int16 | 整数,-32768 至 32767 | 'i2' |
| np.int32 | 整数,-2 31 至 2 32 -1 | 'i4' |
| np.int64 | 整数,-2 63 至 2 63 - 1 | 'i8' |
| np.uint8 | 无符号整数,0 至 255 | 'u' |
| np.uint16 | 无符号整数,0 至 65535 | 'u2' |
| np.uint32 | 无符号整数,0 至 2 ** 32 - 1 | 'u4' |
| np.uint64 | 无符号整数,0 至 2 ** 64 - 1 | 'u8' |
| np.float16 | 半精度浮点数:16位,正负号1位,指数5位,精度10位 | 'f2' |
| np.float32 | 单精度浮点数:32位,正负号1位,指数8位,精度23位 | 'f4' |
| np.float64 | 双精度浮点数:64位,正负号1位,指数11位,精度52位 | 'f8' |
| np.complex64 | 复数,分别用两个32位浮点数表示实部和虚部 | 'c8' |
| np.complex128 | 复数,分别用两个64位浮点数表示实部和虚部 | 'c16' |
| np.object_ | python对象 | 'O' |
| np.string_ | 字符串 | 'S' |
| np.unicode_ | unicode类型 | 'U' |
创建数组的时候指定类型
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]], dtype=np.float32)
>>> a.dtype
dtype('float32')
>>> arr = np.array(['python', 'tensorflow', 'scikit-learn', 'numpy'], dtype = np.string_)
>>> arr
array([b'python', b'tensorflow', b'scikit-learn', b'numpy'], dtype='|S12')
- 注意:若不指定,整数默认int64,小数默认float64
4 总结
知道数组的基本属性,不同形状的维度表示以及数组的类型